
Civil Engineering Team
A leader in the design and implementation of the latest and the most innovative engineering methods

ICE Submarine Services
In partnership with Sharif University of Technology, we have been working for many years in designing and constructing marine structures with different applications in Iran. Based on the experiences we have gained, we decided to extend our field of activity to design and build mini-submarines.
Based on this, we designed and implemented the industrial production process of mini-submarine. The methods used in the design and construction process are very precise and based on international regulations and standards that match the regulations of the destination countries all around the world.
The design is based on computer and field modeling using the most advanced design software, towing tanks, and lake tests. The required materials are procured from large and reliable factories. Afterward, the process of making the structure is completed in the factory, while quality control tests are performed at every stage.
The documentation of all the design stages, including the computer modeling, structure plans, laboratory reports, and the specifications and strength of the material are prepared and sent to the client along with the quality control tests of the manufacturing process. As a result, the quality of all stages of design and construction is guaranteed for the employer.


Underwater Vehicle History
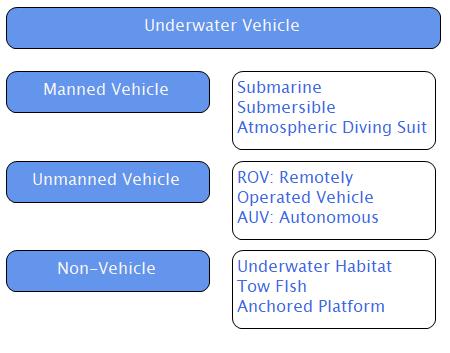
In general, an underwater vehicle is a floating structure that can move on the surface and underwater. This multipurpose floating structure increases the two-directional movement of boats to a three-directional effort by diving into the depths of the sea. Underwater vehicles are categorized into three main fields, as shown in Figure 1. Manned vehicles can carry humans inside, unmanned vehicles are mostly used for exploration issues, and non-vehicles are mostly used for monitoring (US Navy). These explanations are organized in a manner to evaluate available features and to conclude the inventing idea of this project.
One of the first things that significantly impacted this field was the invention of the submarine. A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. Submarines have one of the widest ranges of types and capabilities of any vessel. They range from small autonomous examples and one- or two-person subs that operate for a few hours to vessels that can remain submerged for months.
The submarine, or SUB in the brief literature form, is a specially designed type of watercraft that can submerge and operate completely underwater. Proof exists to support the belief that the first navigable submarine was built by Cornelius Drebbel in 1620, as shown in Figure. In the mid-1700s in England, several submersible watercraft patents had been granted to various inventors, but the first military submarine was invented by an American named David Bushnell in 1775. By 1867 the first submarine powered by combustion, called the Ictineo II, was built in Spain. Navies began using submarines in the early 1900s, and they are commonly used by various militaries worldwide (Gerrit 1932).
Although most of the world's submarines are military, some civilian submarines are used for tourism, exploration, oil and gas platform inspections, and pipeline surveys. The Submarine Voyage ride opened at Disneyland in 1959, although it ran underwater. It was not a true submarine, as it ran on tracks and was open to the atmosphere. The first tourist submarine was Auguste Piccard, which went into service in 1964 at Expo64, as shown in Figure 3. By 1997 45 tourist submarines were operating around the world. Submarines with a crush depth in the range of 400500 feet (120150 m) are operated in several areas worldwide, typically with bottom depths around 100 to 120 feet (30 to 37 m), with a carrying capacity of 50 to 100 passengers. (Schweiz 2016)..

Manned Mini-Submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two up to 6 or 9, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched and recovered and which provide living accommodation for the crew and support staff. Both military and civilian midget submarines have been built. Military types work with surface ships and other submarines as mother ships.
In civilian use, midget submarines are generally called submersibles; commercial submersibles are used in, for example, underwater maintenance, exploration, archaeology, and scientific research. Other commercially available submersibles are marketed as novelty tourist attractions and as specialized tenders for wealthy yacht owners.


ICE Submarine Services
In partnership with Sharif University of Technology, we have been working for many years in designing and constructing marine structures with different applications in Iran. Based on the experiences we have gained, we decided to extend our field of activity to design and build mini-submarines.
Based on this, we designed and implemented the industrial production process of mini-submarine. The methods used in the design and construction process are very precise and based on international regulations and standards that match the regulations of the destination countries all around the world.
The design is based on computer and field modeling using the most advanced design software, towing tanks, and lake tests. The required materials are procured from large and reliable factories. Afterward, the process of making the structure is completed in the factory, while quality control tests are performed at every stage.
The documentation of all the design stages, including the computer modeling, structure plans, laboratory reports, and the specifications and strength of the material are prepared and sent to the client along with the quality control tests of the manufacturing process. As a result, the quality of all stages of design and construction is guaranteed for the employer.


Underwater Vehicle History
In general, an underwater vehicle is a floating structure that can move on the surface and underwater. This multipurpose floating structure increases the two-directional movement of boats to a three-directional effort by diving into the depths of the sea. Underwater vehicles are categorized into three main fields, as shown in Figure 1. Manned vehicles can carry humans inside, unmanned vehicles are mostly used for exploration issues, and non-vehicles are mostly used for monitoring (US Navy). These explanations are organized in a manner to evaluate available features and to conclude the inventing idea of this project.
One of the first things that significantly impacted this field was the invention of the submarine. A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. Submarines have one of the widest ranges of types and capabilities of any vessel. They range from small autonomous examples and one- or two-person subs that operate for a few hours to vessels that can remain submerged for months.
The submarine, or SUB in the brief literature form, is a specially designed type of watercraft that can submerge and operate completely underwater. Proof exists to support the belief that the first navigable submarine was built by Cornelius Drebbel in 1620, as shown in Figure. In the mid-1700s in England, several submersible watercraft patents had been granted to various inventors, but the first military submarine was invented by an American named David Bushnell in 1775. By 1867 the first submarine powered by combustion, called the Ictineo II, was built in Spain. Navies began using submarines in the early 1900s, and they are commonly used by various militaries worldwide (Gerrit 1932).
Although most of the world's submarines are military, some civilian submarines are used for tourism, exploration, oil and gas platform inspections, and pipeline surveys. The Submarine Voyage ride opened at Disneyland in 1959, although it ran underwater. It was not a true submarine, as it ran on tracks and was open to the atmosphere. The first tourist submarine was Auguste Piccard, which went into service in 1964 at Expo64, as shown in Figure 3. By 1997 45 tourist submarines were operating around the world. Submarines with a crush depth in the range of 400500 feet (120150 m) are operated in several areas worldwide, typically with bottom depths around 100 to 120 feet (30 to 37 m), with a carrying capacity of 50 to 100 passengers. (Schweiz 2016)..


ICE Submarine Services
In partnership with Sharif University of Technology, we have been working for many years in designing and constructing marine structures with different applications in Iran. Based on the experiences we have gained, we decided to extend our field of activity to design and build mini-submarines.
Based on this, we designed and implemented the industrial production process of mini-submarine. The methods used in the design and construction process are very precise and based on international regulations and standards that match the regulations of the destination countries all around the world.
The design is based on computer and field modeling using the most advanced design software, towing tanks, and lake tests. The required materials are procured from large and reliable factories. Afterward, the process of making the structure is completed in the factory, while quality control tests are performed at every stage.
The documentation of all the design stages, including the computer modeling, structure plans, laboratory reports, and the specifications and strength of the material are prepared and sent to the client along with the quality control tests of the manufacturing process. As a result, the quality of all stages of design and construction is guaranteed for the employer.
For more than decades, we have exclusively carried out scientific and executive activities related to this field in order to specialize all services provided for you. The services are delivered with the best possible services and the highest standards. We work with great clients and staff to produce excellent work:


Underwater Vehicle History
In general, an underwater vehicle is a floating structure that can move on the surface and underwater. This multipurpose floating structure increases the two-directional movement of boats to a three-directional effort by diving into the depths of the sea. Underwater vehicles are categorized into three main fields, as shown in Figure 1. Manned vehicles can carry humans inside, unmanned vehicles are mostly used for exploration issues, and non-vehicles are mostly used for monitoring (US Navy). These explanations are organized in a manner to evaluate available features and to conclude the inventing idea of this project.
One of the first things that significantly impacted this field was the invention of the submarine. A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. Submarines have one of the widest ranges of types and capabilities of any vessel. They range from small autonomous examples and one- or two-person subs that operate for a few hours to vessels that can remain submerged for months.
The submarine, or SUB in the brief literature form, is a specially designed type of watercraft that can submerge and operate completely underwater. Proof exists to support the belief that the first navigable submarine was built by Cornelius Drebbel in 1620, as shown in Figure. In the mid-1700s in England, several submersible watercraft patents had been granted to various inventors, but the first military submarine was invented by an American named David Bushnell in 1775. By 1867 the first submarine powered by combustion, called the Ictineo II, was built in Spain. Navies began using submarines in the early 1900s, and they are commonly used by various militaries worldwide (Gerrit 1932).
Although most of the world's submarines are military, some civilian submarines are used for tourism, exploration, oil and gas platform inspections, and pipeline surveys. The Submarine Voyage ride opened at Disneyland in 1959, although it ran underwater. It was not a true submarine, as it ran on tracks and was open to the atmosphere. The first tourist submarine was Auguste Piccard, which went into service in 1964 at Expo64, as shown in Figure 3. By 1997 45 tourist submarines were operating around the world. Submarines with a crush depth in the range of 400500 feet (120150 m) are operated in several areas worldwide, typically with bottom depths around 100 to 120 feet (30 to 37 m), with a carrying capacity of 50 to 100 passengers. (Schweiz 2016)..
Nowadays, submarines have one of the widest ranges of types and capabilities of any vessel. They range from small autonomous examples and one- or two-person subs that operate for a few hours to vessels that can remain submerged for six monthssuch as the Russian Typhoon class, the biggest submarines ever built


Manned Mini-Submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two up to 6 or 9, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched and recovered and which provide living accommodation for the crew and support staff. Both military and civilian midget submarines have been built. Military types work with surface ships and other submarines as mother ships.
In civilian use, midget submarines are generally called submersibles; commercial submersibles are used in, for example, underwater maintenance, exploration, archaeology, and scientific research. Other commercially available submersibles are marketed as novelty tourist attractions and as specialized tenders for wealthy yacht owners.
Manned Mini-Submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two up to 6 or 9, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched and recovered and which provide living accommodation for the crew and support staff. Both military and civilian midget submarines have been built. Military types work with surface ships and other submarines as mother ships.
In civilian use, midget submarines are generally called submersibles; commercial submersibles are used in, for example, underwater maintenance, exploration, archaeology, and scientific research. Other commercially available submersibles are marketed as novelty tourist attractions and as specialized tenders for wealthy yacht owners.